
What’s mRNA?
Many people first became familiar with the term “mRNA” when COVID-19 vaccines were rolled out. In the simplest terms, mRNA, which stands for messenger ribonucleic acid, is a genetic material that instructs the cells to make specific proteins.
In the last few years, thousands of scientists around the world have worked to enable the use of mRNA as a possible therapeutic to treat several life-tethering diseases. In this context, the set-up of a process suitable to support mRNA manufacturing up to large scale and GMP-grade is crucial.
Manufacturing process of mRNA
The first step of the manufacturing process starts with the design of a plasmid DNA (pDNA) template, which consists of an RNA polymerase promoter and a specific mRNA sequence. The template pDNA is then amplified, purified and linearized to be used in the further manufacturing step. Following the design and preparation of the DNA template, the linear plasmid DNA has to be transcribed into mRNA. This is usually done by using in vitro transcription (IVT). The synthesis of RNA is achieved through an enzymatic reaction of RNA polymerase and nucleotides. After transcription, the mRNA has to be capped, to protect it from nuclease degradation. The capping reaction can be performed after mRNA synthesis (post-transcriptional capping) or during mRNA polymerization (co-transcriptional capping). To isolate the mRNA, a double-step chromatography strategy is needed and includes both affinity and hydrophobic interaction purification steps. Finally, chromatographic strategies are coupled with tangential flow filtration (TFF) to obtain the mRNA drug substance.
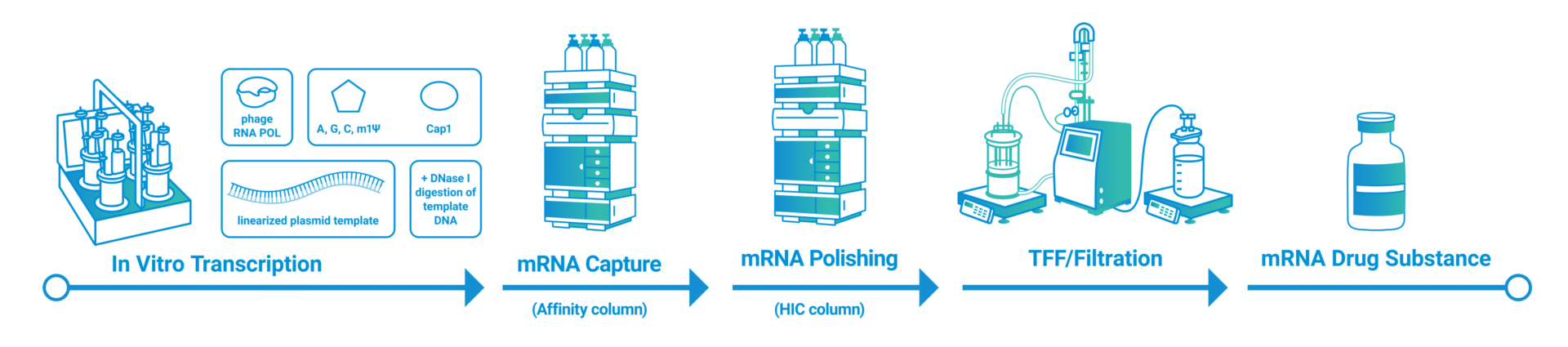
mRNA drug substance is then formulated using lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) and other lipids or carbohydrates which help to deliver the drug safely to the cells. Further, LNPs can help to stabilize the mRNA formulation. After formulation, the drug product is sterilized, aseptically filled and packaged for further storage or transport.
mRNA manufacturing: the next steps
Although the mRNA manufacturing process has been designed and optimized, bottlenecks and challenges are still present and need to be overcome. Even if the COVID vaccines boosted mRNA therapies, there is a constant need to scale up, innovate and improve the mRNA production process to pave the way towards the manufacturing of tomorrow’s drugs.